Carbon black is raw material composed mainly of carbon and as its name indicates, it is black.
Many black objects contain carbon black.
Carbon black is a raw material closely involved in our daily lives.
Carbon black products manufactured by us are used for tires around the world, in a wide range of rubber products, in pigments, and in other numerous products.
Carbon black properties
Carbon black properties are divided into physicochemical and compound properties.
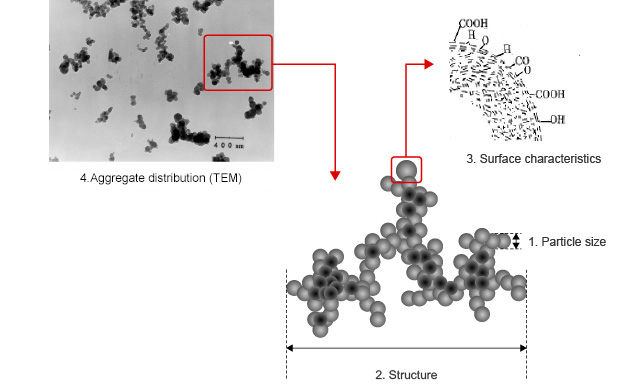
Physicochemical properties
1. Particle size
This refers to the size of an individual particle of carbon black, the smaller the particle size the larger the specific surface.
2. Structure
This shows the state of particles adhered to others of similar size and also indicates oil absorption. The greater the oil absorption, the more complex the configuration.
3. Surface characteristic
Various functional groups are combined on the surface of carbon black, by modifying the surface properties, we can change the compound characteristics.
4. Aggregate distribution
The size of the aggregates (individual carbon black particles fused to other particles of a similar size) varies.
If the distribution is sharp, this indicates that there are many aggregates of the same size.
Compound characteristics
1. Reinforcement
Carbon black is added to the rubber used in tire treads, to high-pressure hoses, and has other demanding applications, as well as added to plastics as material reinforcement.
This characteristic can be divided into carbon black and material physical adsorption (depending on the carbon black's particle size and structure), and carbon black's particle surface and material chemical reaction (depending on the carbon black's surface properties).
2. Conductivity
Conductive carbon black is added to natural rubber or other materials to decrease their electrical resistance.
For example: the conductivity of natural rubber is 1015Ωcm, whereas the conductivity of conductive rubber (natural rubber + conductive carbon black) is between 1-1015Ωcm.
It is believed that this characteristic is the result of the structure of carbon black particles contacting each other which forms conductive channels or because of the "tunnel effect" of electrons jumping between dispersed carbon black particles.
3. Pigmentation
Carbon black has strong tint properties, it is heat stable and suitable for plastic and film coloring.
This property is believed to result from the particle size and the structure's interaction with light.
4. Preventive properties against ultraviolet degradation
Carbon black's absorption of ultraviolet light is excellent. Adding carbon black to other materials prevents ultraviolet degradation.
This is due to stress-fissure prevention in plastics with carbon black, which refines their crystals.


















